1. Introduction
Blockchain is a decentralized and distributed digital ledger technology designed to record transactions securely and transparently across multiple computers. Unlike traditional systems that rely on a central authority, blockchain operates on a peer-to-peer network, ensuring that no single entity holds control over the entire system. This structure makes it highly resilient to fraud and manipulation, as the integrity of the system is maintained through consensus among participants.
The importance of blockchain lies in its ability to ensure security, transparency, and immutability. Each transaction added to the blockchain is time-stamped and linked to the previous one, creating a chronological chain of events that cannot be altered without the approval of the majority of the network. This immutability, combined with transparent transaction visibility, makes blockchain a highly reliable and trustworthy system for various industries.
2. Definition and Structure of Blockchain
Overview of Blockchain
A blockchain is essentially a chain of digital records, known as blocks, that are linked together using cryptographic techniques. These blocks store transaction data, ensuring that each record is secure, traceable, and resistant to tampering. The system’s decentralized nature means that multiple computers (nodes) maintain copies of this ledger, and any new data added must be verified by consensus, ensuring the integrity of the entire chain.
Detailed Explanation of Components
- Data (Transaction Details): Each block contains data related to a specific transaction or set of transactions. This could range from financial transactions to records of asset transfers, making blockchain adaptable for different applications.
- Hash of the Previous Block: One of the key elements of blockchain security is the cryptographic hash that links each block to the previous one. This hash is unique to every block and acts as a digital fingerprint. Any attempt to alter a block would change its hash, breaking the chain and alerting the network to potential tampering.
- Timestamp: Every block is marked with a timestamp, which records the exact moment it was added to the blockchain. This ensures a clear chronological order of events, allowing participants to track and verify the history of all transactions.
How These Components Form a Secure and Tamper-Proof Chain
The combination of transaction data, cryptographic hashes, and timestamps creates a structure where altering one block would require changing every subsequent block in the chain. This is practically impossible without the consensus of the majority of participants in the network, making blockchain highly secure. This tamper-proof structure is what sets blockchain apart from traditional databases, offering an unparalleled level of data integrity and trust.
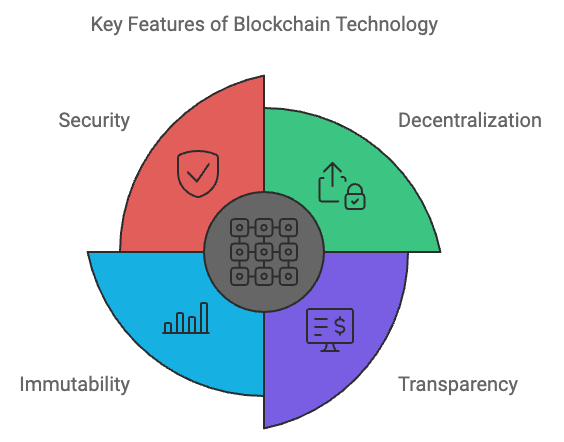
3. Key Features of Blockchain
Decentralization
Blockchain operates on a peer-to-peer (P2P) network, meaning that data is distributed across multiple computers (or nodes) rather than being stored in a central location. Unlike traditional databases, which are controlled by a single authority, blockchain’s decentralized nature eliminates the need for intermediaries and reduces the risk of a single point of failure. Each node in the network holds an identical copy of the blockchain, and any updates to the ledger are verified through a consensus mechanism. This decentralization strengthens security, trust, and resilience, making blockchain less vulnerable to attacks or corruption compared to traditional systems.
Immutability
One of the most critical features of blockchain is its immutability. Once a transaction is recorded in a block and added to the chain, it becomes nearly impossible to alter or delete. This is achieved through cryptographic hashing, which ties each block to its predecessor. To modify a single transaction, a user would need to alter not only that specific block but every block that follows, which would require an immense amount of computational power and network consensus. This unchangeable nature of blockchain makes it an ideal solution for applications that require a high level of trust, such as financial transactions, legal agreements, and record-keeping.
Transparency
Blockchain promotes transparency by allowing all participants in the network to view the entire history of transactions. Each node in the decentralized network holds a copy of the blockchain, and any updates to the ledger are publicly available. This open visibility helps create an environment of accountability and trust among participants, as discrepancies can be quickly identified and addressed. Transparency is a key reason why blockchain is increasingly being adopted in industries where fraud prevention and public trust are critical, such as finance and supply chain management.
Consensus Mechanisms
Blockchain relies on various consensus mechanisms to validate transactions and maintain the integrity of the ledger. Two of the most common methods are:
- Proof of Work (PoW): This is the original consensus mechanism used by Bitcoin. In PoW, network participants (miners) compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and add new blocks to the chain. The first miner to solve the puzzle is rewarded, and the block is added to the blockchain. While secure, PoW is energy-intensive and requires significant computational resources.
- Proof of Stake (PoS): PoS is an alternative consensus mechanism where validators are chosen based on the number of coins they hold (stake) rather than solving puzzles. Validators are rewarded for adding new blocks, and the system requires less energy than PoW. PoS is increasingly favored for its energy efficiency and scalability.
Both mechanisms ensure that all nodes in the network agree on the current state of the blockchain, preventing tampering and fraud.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms and conditions directly written into code. These contracts automatically enforce and execute agreements when predefined conditions are met, removing the need for intermediaries like lawyers or escrow agents. For example, a smart contract could release payment for a service only after the service has been confirmed as delivered. This automation increases efficiency, reduces costs, and eliminates the potential for human error or manipulation in executing agreements.
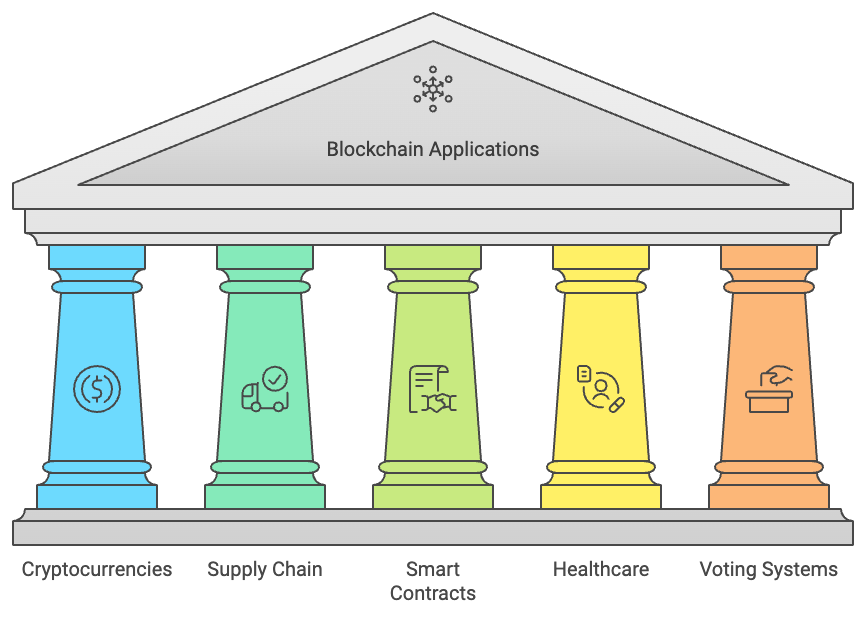
4. Applications of Blockchain Technology
Finance
In the financial sector, blockchain is transforming how transactions are processed, particularly in cross-border payments. Traditional methods for transferring funds across countries can be slow, costly, and prone to fraud. Blockchain streamlines this process by providing a secure and efficient way to verify transactions without the need for intermediaries like banks. Additionally, blockchain’s immutability reduces the risk of fraud, ensuring that transactions cannot be tampered with once they are recorded.
Supply Chain Management
Blockchain is revolutionizing supply chain management by improving the traceability of goods. Companies can use blockchain to record the journey of products from origin to destination, ensuring transparency at every step. This reduces the risk of fraud, theft, and counterfeiting, while also making it easier to identify and resolve errors in the supply chain. For instance, if a batch of goods is recalled, blockchain can quickly trace the specific lot, improving efficiency and accuracy.
Healthcare
In healthcare, blockchain offers a secure way to store and manage patient records. Sensitive data, such as medical histories and test results, can be stored on a blockchain, ensuring that only authorized personnel can access it. Blockchain’s decentralized and immutable structure makes it nearly impossible for unauthorized parties to alter or access these records, providing a high level of privacy and security. This is especially important in protecting patient data from cyberattacks.
Real Estate
Blockchain is streamlining real estate transactions by providing a clear, tamper-proof record of property ownership. Traditional real estate transactions often involve intermediaries such as title companies, which can add time and costs to the process. With blockchain, ownership records are securely stored and easily verifiable, reducing the need for third-party validation. This results in faster, more efficient property transfers with reduced costs and fewer opportunities for fraud.
Voting Systems
One of the most promising applications of blockchain is in voting systems. Traditional voting methods are susceptible to fraud, tampering, and lack of transparency. Blockchain offers a secure, transparent, and tamper-proof solution for electoral processes. Votes can be recorded on a blockchain, where they are immutable and publicly verifiable, ensuring that election results are accurate and transparent. This technology could revolutionize how elections are conducted, increasing public trust in democratic processes.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology represents a paradigm shift in how data is managed, secured, and shared across a wide range of industries. By offering key features such as decentralization, immutability, transparency, and the ability to create and execute smart contracts, blockchain has transformed traditional models of record-keeping and transactions. Its use in sectors like finance, supply chain management, healthcare, real estate, and voting systems showcases its immense potential to enhance security, efficiency, and trust.
As more industries explore and implement blockchain solutions, the impact of this technology is expected to grow, offering novel solutions to long-standing challenges in data integrity, fraud prevention, and operational efficiency.
Further Reading and Resources
For readers interested in deepening their understanding of blockchain technology, the following resources provide excellent insights:
- Wikipedia on Blockchain: A comprehensive overview of blockchain’s history, functionality, and applications. Wikipedia Link
- Investopedia’s Overview: An accessible introduction to blockchain, its key concepts, and its relevance to various industries. Investopedia Link
- TechTarget’s Explanation: A deep dive into how blockchain works and its key features. TechTarget Link
- IBM’s Insights on Blockchain: Detailed examples of how blockchain is being applied across different industries. IBM Link
- Built In’s Comprehensive Guide: A guide that explores the different types of blockchain and its real-world applications. Built In Link
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- What is the main purpose of a blockchain system? A blockchain system is primarily used to provide a decentralized, secure, and transparent way of recording transactions. It ensures data integrity and eliminates the need for intermediaries.
- How does blockchain ensure data security and immutability? Blockchain uses cryptographic hashing to link each block to the previous one, making it extremely difficult to alter data without changing every subsequent block. This guarantees that once data is recorded, it cannot be tampered with.
- What are the key advantages of blockchain over traditional databases? Blockchain offers decentralization, which eliminates the need for a central authority, immutability, ensuring data cannot be changed, and transparency, allowing all participants to see transactions and ensuring accountability.
- How do consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work and Proof of Stake work in blockchain? Proof of Work (PoW) requires miners to solve complex puzzles to validate transactions, while Proof of Stake (PoS) selects validators based on their stake in the network. Both mechanisms ensure that all nodes agree on the state of the blockchain.
- What are the most common applications of blockchain technology? Blockchain is widely used in finance for cross-border payments, supply chain management for tracking goods, healthcare for securing patient records, real estate for property transactions, and voting systems for ensuring fair and tamper-proof elections.